Original Article
, Volume: 15( 4)Study of Features of Pyrotechnic Gas Generating Burning Compositions
- *Correspondence:
- Tulepov MI Al-Farabi National University, Almaty, Kazakhstan, Tel: +7-7272211000; E-mail: tulepov@rambler.ru
Received: April 13, 2017; Accepted: November 07, 2017; Published: November 10, 2017
Citation: Baiseitov DA, Tulepov MI, Kazakov Y, et al. Study of Features of Pyrotechnic Gas Generating Burning Compositions. Int J Chem Sci. 2017;15(4):218.
Abstract
In the work the basic laws and features of combustion of pyrotechnic gas generating compositions were researched. On the basis of thermodynamic calculations of characteristics of combustion of the pyrotechnic gas-generating the components and their ratios for preparation of gas generating compositions: ammonium nitrate-an oxidizer, coal arenas-the fuel-binder, melamine and polyvinyl alcohol-gasification supplements were found. Two formulations were developed and researched. It was revealed that the compressive strength of compositions of pyrotechnic products is provided by cementators (coal arenas).
Keywords
Pyrotechnic; Burning; Explosives; Ammonium nitrate
Introduction
Application of pyrotechnic gas generating mixtures on the basis of ammonium nitrate is one of the perspective methods reducing the harmful effects of explosive gases on the ecology and the cost price of ore mining, the energy intensity of mining operations and improving the safety of their implementation [1-3]. Availability, simplicity and safety of the technology of production and obtaining of ammonium nitrate in the manufacture of explosives (E) led to its mass application. Also, the fact that ammonium nitrate in pure form is explosive is important: a heat of its explosion of 335 kcal/kg that is about 3 times less than heat of explosion of a trotyl, operability (explosive fragmentation) in a lead bomb of Trautsl is equal to 165 cm3-230 cm3. The detonation rate is of the order of 1.5 kms-2.5 kms, which requires for its explosion presence of an intermediate detonator from the powerful E [4]. The high level of temperature of the generated gas is characteristic of pyrotechnic generators of traditional type of combustion that significantly limits the field of their application and forces to use in some cases gas-balloon devices, despite their shortcomings. Application of the producer-gas chemical cartridges (PGCC) has particular restrictions: obligatory requires the dense tamping of hole by sand (granite screenings) and sufficient depth of the hole. The first relates to the fact that the pressure exerted during combustion of the composition of the gas generator, can develop only in the closed volume.
The second condition is due to both the magnitude of pressure developed during combustion and with the pace of its growth and is determined by the frictional force tamping on the walls of the hole. Therefore, before starting the main work must be carried out the tuning tests to determine of these conditions, especially in the destruction of objects with unknown structure of reinforcement [1,2]. The work purpose studying of the main regularities and features of combustion of the pyrotechnic gas-generating compositions.
Experimental
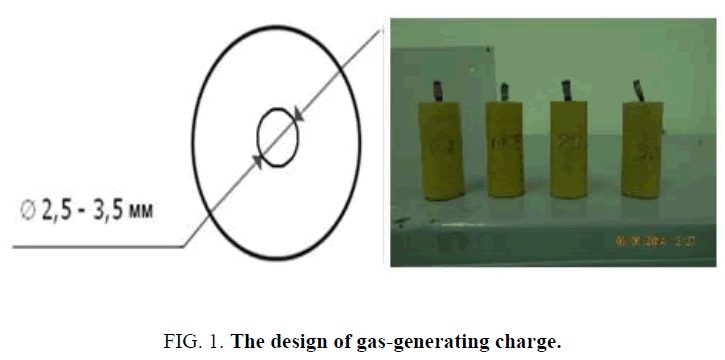
For research of the processes of combustion of the gas generating charge a construction has been made, which ensures combustion of charge for 1.5 seconds at a pressure within the chamber-not more than 2 MPa (FIG. 1 ). The presence of the channel inside gas-generating charge causes a rapid combustion due to reducing of thickness of the conflagrant vault up to 4.5 mm.
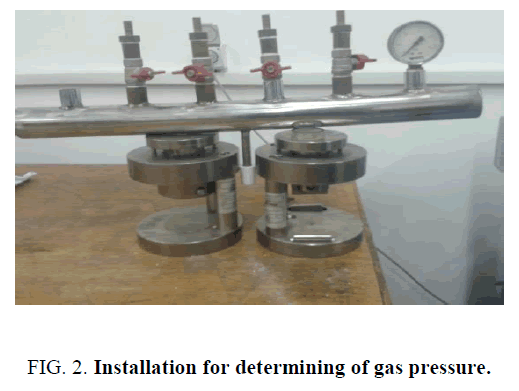
FIG. 2 shows a device for determining the pressure of the gases released in the combustion of pyrotechnic gas generating compositions. Combustion was initiated with the help of tungsten spiral. The pressure of the gases released are recorded by means of manometer.
In the work theoretical and experimental researches of combustion of gas-forming composites were carried out. The thermodynamics calculations of the characteristics (adiabatic temperature of burning and equilibrium composition of products) of pyrotechnic compositions with the use of complex of the programs "Thermo" on the base of the method of minimization of thermodynamics potential of energy of Gibbs were performed. Initial components for development of compounding of gas-forming compositions: ammonium nitrate: an oxidizer, coal arenas: both fuel and binder, melamine, dicyandiamide, polyvinyl alcohol-gasification supplements were chosen [5].
The combustion temperature was measured by chromel-aluminum thermocouple. The burning rate was measured as follows: pyrotechnic compositions were placed in a thick-walled pipe with a diameter of 1.5 cm; with a height of 22.7 cm. Combustion was initiated with the upper part of the tube with the initiating composition (50% Mg+50% smokeless powder). The burning rate is determined by dividing the height of the compositions of the pipe at the time of combustion compositions. The pressure of released gases was measured on the installation, which was designed and mounted in the laboratory. The first series of thermodynamic calculations was carried out for the base mixture "oxidizer-fuel" for different ratios of the components. The second series of calculations was carried out for the triple mixtures "oxidizer-fuel-gasifying agent" for different ratios of the components. The following systems: 1. KNO3-Mg-smokeless powder-coal arenas, 2. KNO3-coal arenas were taken for determination of the strength characteristics of the pyrotechnic compositions.
Results and Discussion
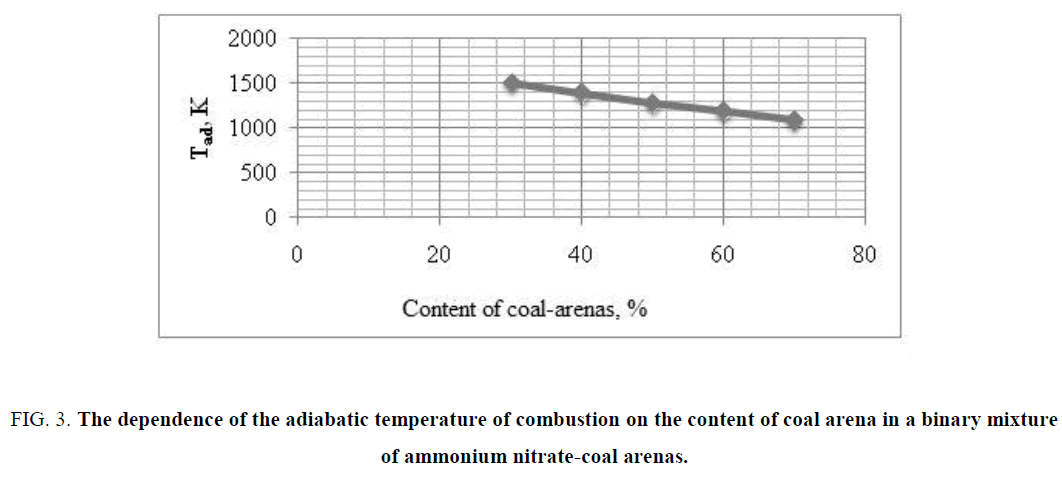
It was found on the base of thermodynamics calculations of adiabatic temperature of burning of binary mixture of ammonium nitrate-coal arenas, that adiabatic temperature of burning is decreased from 1521 K to 1162 K with increasing of coal arena content. These data were used to develop recipes of pyrotechnic gas of generating composition with the low temperature of the generated gas. The results of calculation of the adiabatic temperature of combustion of binary mixture of ammonium nitrate-coal arenas are presented in FIG. 3. Results of calculation of composition of gaseous products of burning of double mixture ammonium nitrate-coal arenas are shown in TABLE 1.
FIG. 3: The dependence of the adiabatic temperature of combustion on the content of coal arena in a binary mixture of ammonium nitrate-coal arenas.
| Content of coal-arene, % | Products of combustion, % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methane | Carbon oxide | Carbon dioxide | Hydrogen | Nitrogen | Water vapor | |
| 30.0 | 0.58 | 53.0 | 0.5 | 31.7 | 13.4 | 0.82 |
| 40.0 | 2.15 | 45.13 | 1.26 | 38.0 | 11.2 | 2.26 |
| 50.0 | 4.33 | 37.87 | 2.57 | 41.15 | 9.27 | 4.81 |
| 60.0 | 7.44 | 30.14 | 3.99 | 42.92 | 7.39 | 8.12 |
| 70.0 | 11.0 | 23.6 | 4.87 | 43.83 | 5.5 | 11.2 |
TABLE 1. The calculated composition of the gaseous products of combustion of binary mixture ammonium nitrate-coal arenas.
It is shown on the basis of thermodynamic calculations of equilibrium composition of the combustion products that in the basis of the products of combustion of binary mixture of ammonium nitrate-coal arenas comprised carbon monoxide and hydrogen. Also in appreciable quantities nitrogen methane, carbon dioxide and water vapours are formed, thus the proportion of the latter is increased with increasing of coal arene content.
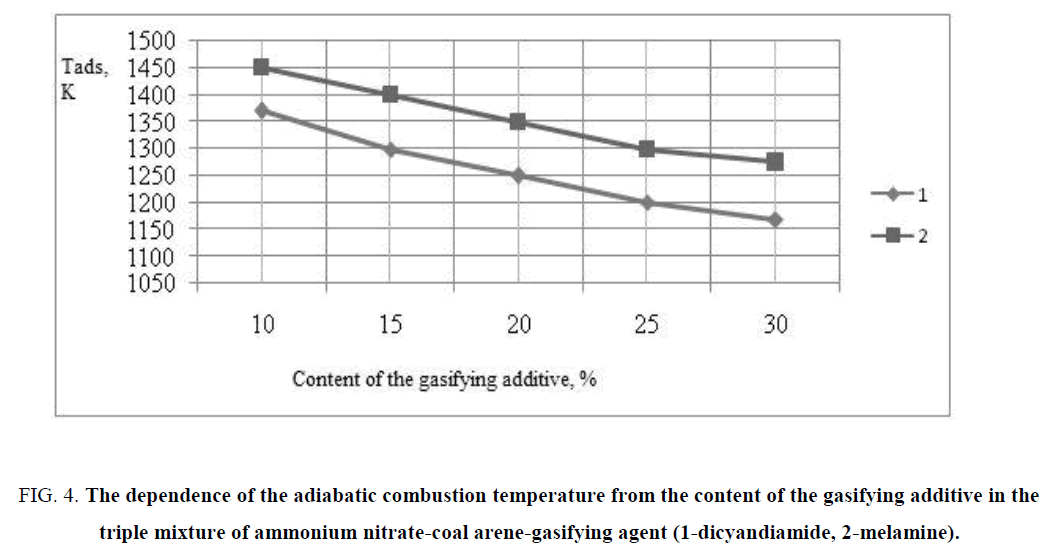
The results of calculation of the adiabatic combustion temperature of triple mixtures of ammonium nitrate-coal arenas-gasifying additive are presented in FIG. 4.
FIG. 4: The dependence of the adiabatic combustion temperature from the content of the gasifying additive in the triple mixture of ammonium nitrate-coal arene-gasifying agent (1-dicyandiamide, 2-melamine).
It is revealed on the basis of the thermodynamic calculations that the adiabatic combustion temperature depended on the content of additives in the gasifying of the triply mixtures, the lowest temperature is observed in the triple mixtures with melamine (1170 K-1370 K), thus the temperature decrease is observed with increasing of content of melamine in the triple mixture. The basis of products of burning of triple mixtures is constituted by the oxide of carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, thus increase of content of the latter was due to the use of the nitrogen compounds as the gasifying additives (TABLE 2).
| Content of acetic acid, % | Products of combustion, % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methane | Carbon oxide | Carbon dioxide | Hydrogen | Nitrogen | Water vapour | |
| 10.0 | 1.38 | 49.34 | 1.74 | 29.39 | 16.02 | 2.13 |
| 15.0 | 1.3 | 46.79 | 3.11 | 27.54 | 17.52 | 3.31 |
| 20.0 | 2.14 | 43.18 | 4.91 | 26.28 | 18.77 | 4.72 |
| 25.0 | 2.59 | 38.29 | 7.51 | 24.41 | 20.61 | 6.59 |
| 30.0 | 2.69 | 35.55 | 9.29 | 22.75 | 22.11 | 7.61 |
TABLE 2. The calculated composition of gaseous products of burning of triple mixture ammonium nitrate-coal arenas melamine.
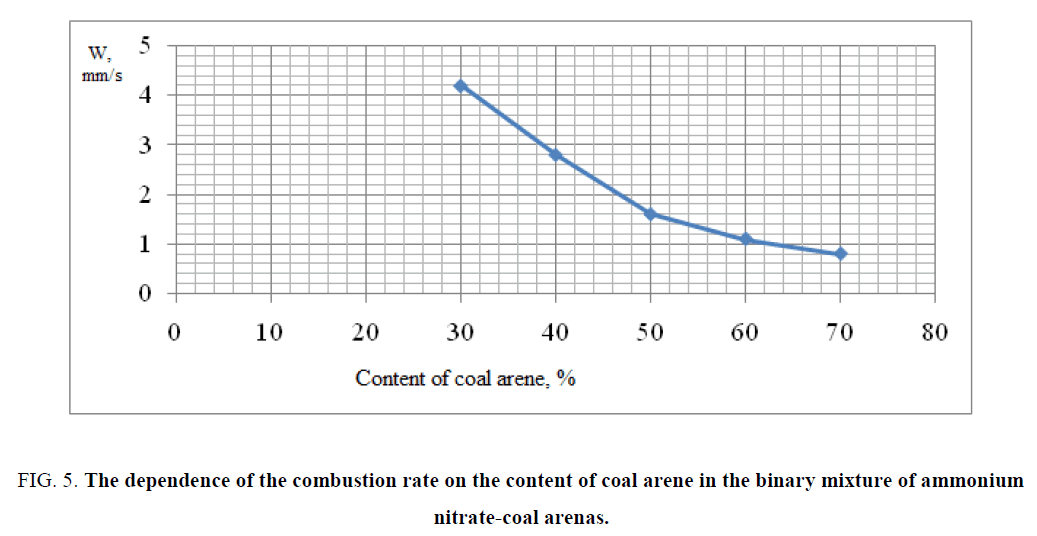
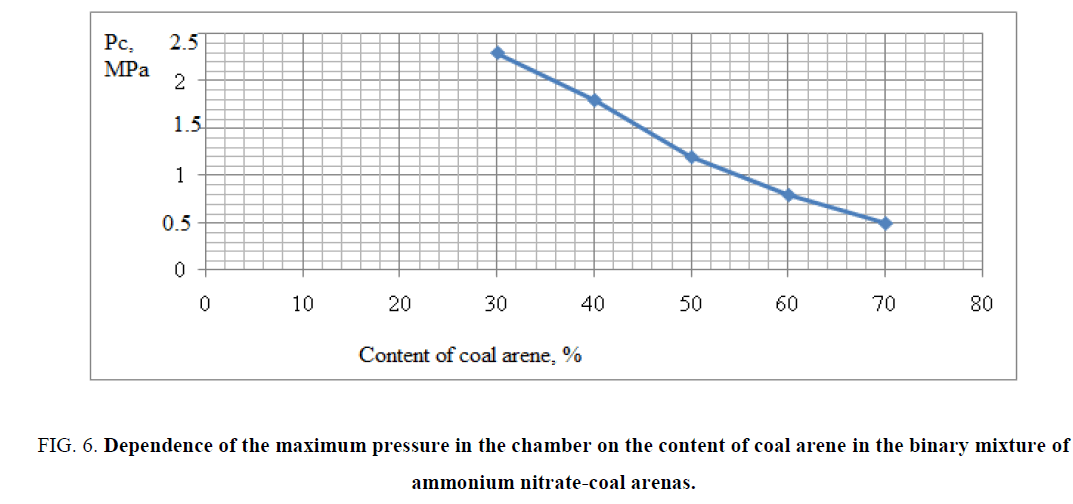
The obtained experimental results of combustion of binary mixtures are shown in FIG. 5,6 . The data of FIG. 5,6 shows that the optimal composition for a large amount of gas evolution and maximum combustion rate was for the composition containing 30% coal arene and 70% ammonium nitrate. By results of researches as the basis of a ternary mixture was chosen the binary mixture of ammonium nitrate/coal arene=70/30, because for this mixture possessed the highest rate of combustion and very high specific gas capacity of the studied binary mixtures. The experimental data confirmed the choice as a fuel and at the same time the binder coal arene, which was as a reactor stratum. As a result of the reaction of coal arene with ammonium nitrate the solid wastes are formed and the formation of durable porous framework is formed preventing entrainment of condensed reaction products from the combustion zone.
FIG. 5: The dependence of the combustion rate on the content of coal arene in the binary mixture of ammonium nitrate-coal arenas.
FIG. 6: Dependence of the maximum pressure in the chamber on the content of coal arene in the binary mixture of ammonium nitrate-coal arenas.
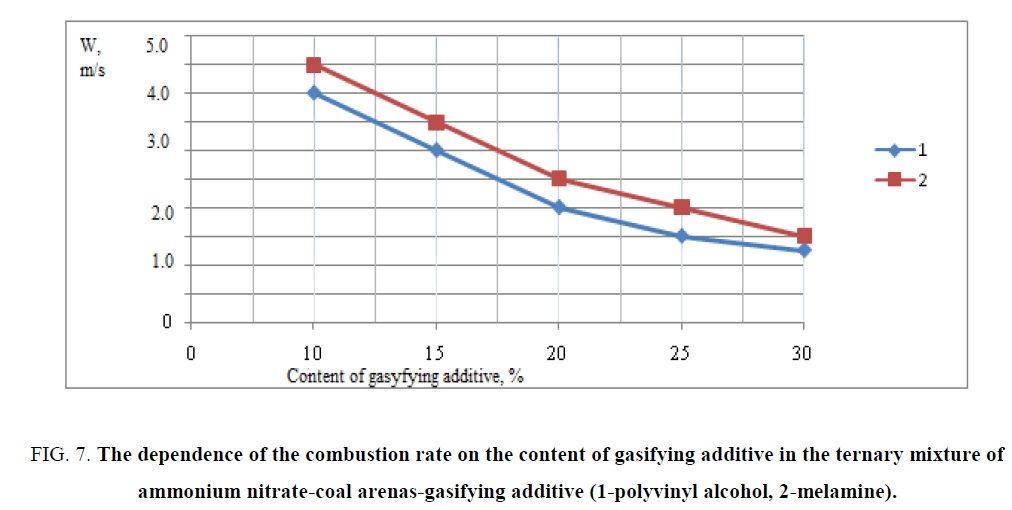
The frame as a block is remained in the chamber before the filter and to the receiver container through the filter are entered only the gaseous products of gasification. Therefore, the filter is necessary to cool the already partially cooled pure gas without condensed impurities. The results of combustion of triple mixtures are shown in FIG. 7. The temperatures of burning of triple mixtures are experimentally determined with the content of gasifying additive polyvinyl alcohol and melamine according to which the temperature of combustion mixture is dependent on the content of gasifying additive and its decrease is observed with an increase in the content of additives. The combustion temperature of researching triple mixtures with polyvinyl alcohol was 423 K-723 K and with melamine -423 K-673 K. The data of the research show that the optimal composition for a large amount of gas evolution and maximum combustion rate was a composition containing 10% of the gasifying agent (polyvinyl alcohol), 70% ammonium nitrate and 20% coal arene. According to the research as the basis of a ternary mixture was chosen triple mixture of ammonium nitrate/coal arene/polyvinyl alcohol=70/20/10, the mixture had the highest rate of combustion of the investigated ternary mixtures.
FIG. 7: The dependence of the combustion rate on the content of gasifying additive in the ternary mixture of ammonium nitrate-coal arenas-gasifying additive (1-polyvinyl alcohol, 2-melamine).
The researches allowed to develop two formulation of the gas generating composition, which ensure the necessary values for the rate of combustion-chamber pressure and temperature of the generated gas:
| Recipe Formulation #1 | Recipe Formulation #2 |
| -Ammonium nitrate-58 (± 4)% | -Ammonium nitrate-58 (± 4)% |
| -Coal arenas-25 (± 3)% | -Coal arenas-25 (± 3)% |
| -Polyvinylalcohol-17 (± 3)% | -Melamine-15 (3)% |
| -Graphite-1% more than 100 | -Graphite-1% more than 100. |
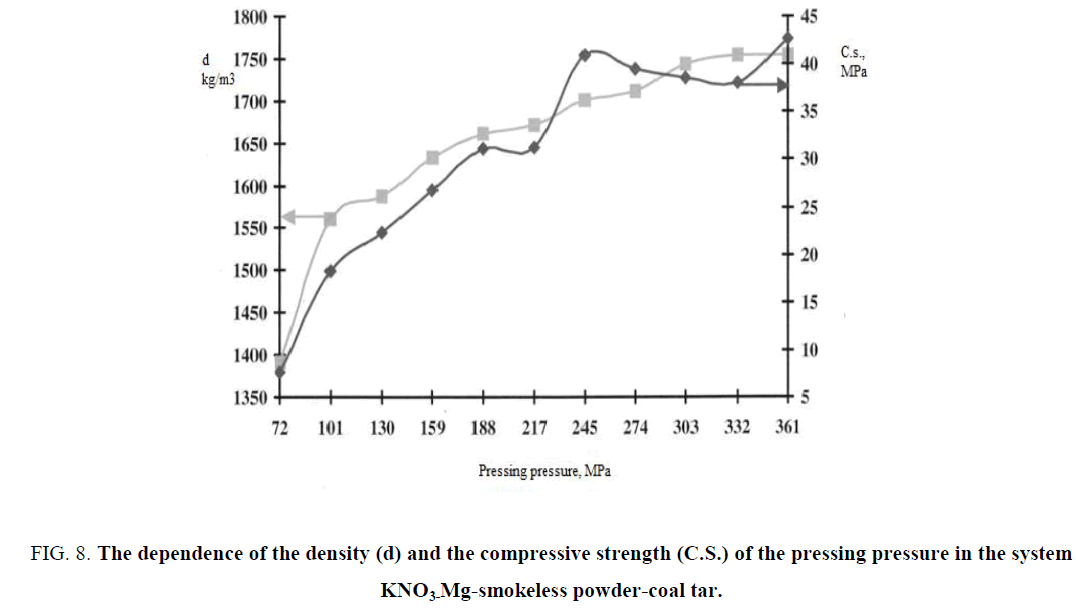
The specific density and the compressive strength of the pyrotechnic products with application of various polymeric binders were measured for determination of the dependence of the strength of finished products from the pressing pressure, that ultimately led to the implementation of a technological process of pressing of pyrotechnic articles and in particular the choice of pressing equipment. It was tested the system ?NO3-Mg which was presented a smokeless powder, in that as a binder coal tar is used. In FIG. 8 dependences of density and pressed strength in the given system were presented.
FIG. 8: The dependence of the density (d) and the compressive strength (C.S.) of the pressing pressure in the system KNO3-Mg-smokeless powder-coal tar.
Ranging from 70 MPa compaction pressure the density of the sample was sufficiently fast growing and reached a limit of the corresponding to 1730 kg/m3 at 300 MPa the pressing pressure. The further increase of the pressing pressure to an appreciable increase in the density didn't lead. The compressive strength of the sample also increases monotonically to a point in which the compacting pressure of 245 MPa correspondence value after that remains at the same level. In this case, the main component responsible for the strength of the composite article is a resin. Resin apparently, with a pressure over 230 MPa-240 MPa is considerably deformed and wraps around all elements of a composite product. That is, the pressing condition value exceeds a plastic deformation for that substance.
For determination of the safety of use and manufacturing of the developed gas-forming compositions the tests on sensitivity to shock and friction were carried out. The tests showed that the developed gas-forming compositions are insensitive to shock (explosion frequency in the instrument 1 is 0%) and friction at a shock shift (relative frequency of explosions at a pressure of pressing Psn=353 MPa (3600 kgf/cm2) was equal to 0%).
The thermal stability and sensitivity of the developed gas-forming composition to the thermal effects of the method of differential thermal analysis of high resolution were studied. The conducted differential thermal analysis of a high resolution showed the high thermal stability and low sensitivity to thermal effects of the elaborated gas-forming compositions. The obtained values of the flash temperature (396 ± 10°C) and of the activation energy (309.9 kJ/mmol) of compositions are indirect characteristic of stability of the working descriptions of the gas generating charges on the basis of the developed recipes of the gas-forming compositions in the process of prolonged storage.
Conclusion
On the basis of thermodynamic calculations of the pyrotechnics gas generating compositions the components and their ratios for synthesis formulations of gas generating compositions: ammonium nitrate, an oxidizer, coal arenas: the fuel-binder, melamine and polyvinyl alcohol-gasification supplements were found. The laws of combustion of pyrotechnic gas generating compositions were determined and two formulations of gas-forming compounds: 1) ammonium nitrate-58 (± 4)%, coal arenas-25 (± 3)%, polyvinyl alcohol-17 (± 3)%, graphite-1% excess weight, 2) ammonia nitrate-65 (± 4)%, coal arenas-20 (± 3)%, melamine-15 (3)% graphite-1% over 100 were developed and comprehensively studied. Results of the study of dependencies of the compressive strength of the pressing pressure show that the composite strength of pyrotechnic products is provided by cementators (coal arenas). For determination of the safety of use and manufacturing of the developed gas-forming compositions the tests on sensitivity to shock and friction were carried out. The experiments showed that the developed gas-forming compositions are insensitive to shock (explosion frequency in the instrument 1 is 0%) and friction at a shock shift (relative frequency of explosions at a pressure of pressing Psn=353 MPa (3600 kgf/cm2) was equal to 0%).
References
- Agaphonov NN. Academic Methodical Manual. Nedra M.1993;pp:72.
- Massenova AT, Sassykova LR, Kassenova D. Europacat-5. Limerick, Ireland. 2001;pp:16-24.
- Gorbovskiy K, Kazakov A, Norov A, et al. Properties of complex ammonium nitrate-based fertilizers depending on the degree of phosphoric acid ammoniation. International Journal of Industrial Chemistry. 2017;8(3):315-27.
- Kazakov YV. Thesis of diss of Cand. Chem Sci Alma-Ata. 1994.
- Baiseitov DA,Tulepov MI, Kazakov Y, et al. News of NAS of RK. Ser Chem Technol. 2015;409:85-91.