Original Article
, Volume: 12( 6)A Brief Review: Microwave Assisted Ethers Synthesis
- *Correspondence:
- Kazemi M , Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Basic Sciences, Ilam University, P.O.Box-69315516, Ilam, Iran, Tel: 98(841)2227010; E-mail: Mosstafakazemi@gmail.com
Received: October 06, 2016; Accepted: November 16, 2016; Published: November 22, 2016
Citation: Kazemi M, Shiri L, Heidari L. A Brief Review: Microwave Assisted Ethers Synthesis. Org Chem Ind J. 2016;12(6):107.
Abstract
Ethers play a key role in the synthesis of pharmaceutical, biological, industrial, and natural products. This review paper describes the survey of literature regarding the number of microwave techniques for the synthesis of ethers in the recent times.
Keywords
Ethers; Pharmaceutical; Microwave synthesis
Introduction
Carbon-oxygen bond formation is a valuable reaction in organic synthesis and has generated considerable interest in recent years. Ethers are significant solvents and synthetic important supplements for the production of fragrances, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs [1,2]. The Williamson reaction is the best technique for the synthesis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. The Williamson reaction generally involves the employment of an alkali-metal salt of the hydroxyl compound and an alkyl halide. These reactions are generally carried out using organic solvents or with phase-transfer catalysts in the presence of a base followed by refluxing for times long [3-6]. Ether formation can also be accomplished using green solvents, ionic liquids, Mitsunobu reaction, coupling processes, ultrasonic reactions and solvent-free conditions [7-11]. Over the last decades, green Chemistry has become a research field of great interest. The enhancing requirement to minimize pollution and its influences, and the consequent risk for the human health and the environment, has brought towards a novel and safer procedure to chemical processes and compounds, defined in the principles of Green Chemistry. For this purpose, microwave technology, one of synthetic green techniques, has been successfully applied in organic chemistry.
The start of the fast growth of microwave assisted protocols in organic synthesis was ignited in 1986 by pioneering papers by Gedye et al. [12]. The uptake of microwave chemistry as a general means in synthesis laboratories has been gradual and steady since the introduction of chemical microwave systems [13]. The microwave offer easy, clean, speed, convenient, and economic techniques for the synthesis of a large number of organic compounds [14]. Microwave synthesis is obtaining importance as an instrument for the synthesis of a wide range of valuable and important compounds [15]. Now, in this paper, we wish to investigate microwave techniques for the synthesis of ethers derivatives and we will study results and benefits of these techniques.
The synthesis of ethers using microwave techniques
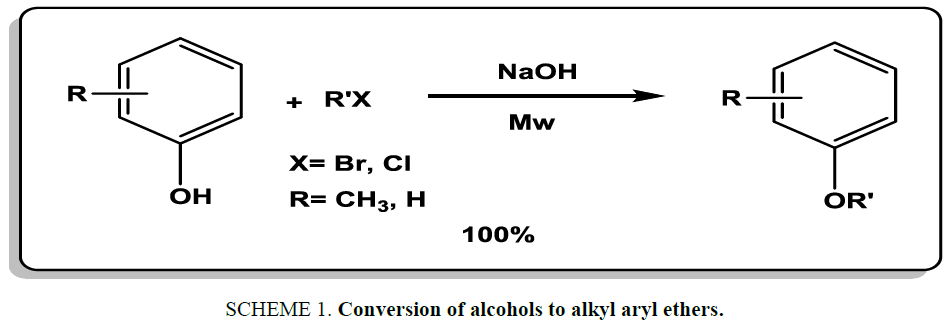
Alkylation alcohols are the most common strategy for synthesis of alkyl aryl ethers. For example, Wang et al. [16] used microwave irradiation in the presence of sodium hydroxide for the conversion of alcohols to alkyl aryl ethers. The reactions were carried out in less than 5 min at room temperature (Scheme 1). Products were isolated in excellent yields (78% to 100%).
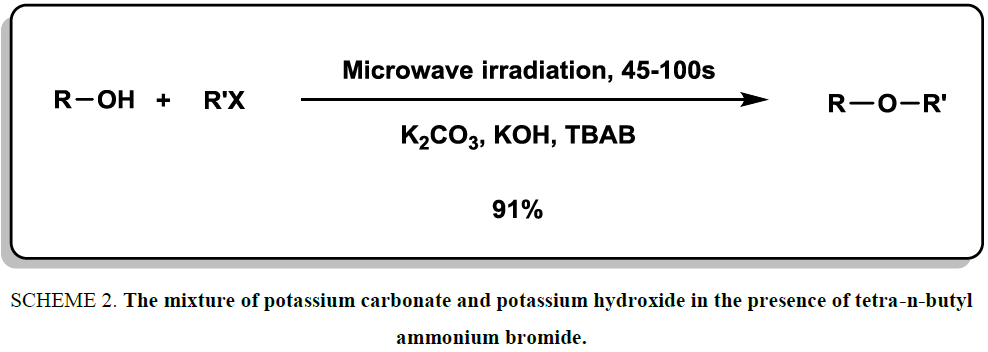
In the year of 1998, a mild and rapid strategy was reported for the synthesis of various ether derivatives [17]. The mixture of potassium carbonate and potassium hydroxide in the presence of tetra-n-butyl ammonium bromide was introduced as an efficient and valuable system to synthesize symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers in high yields. The reactions were accomplished under microwave irradiation (Scheme 2). The variety of products, short reaction times (45-100 second) and use of mild conditions were the most important indices of this methodology.
Scheme 2: The mixture of potassium carbonate and potassium hydroxide in the presence of tetra-n-butyl ammonium bromide.
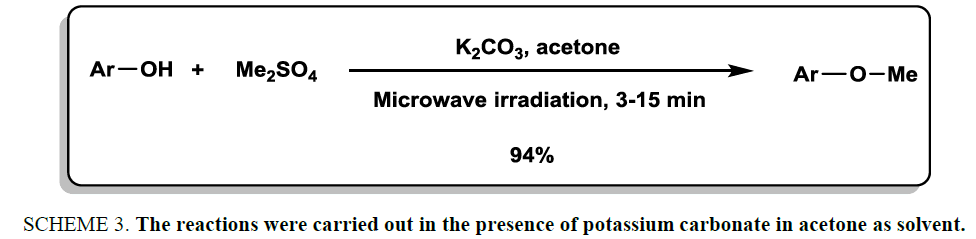
In 2000, Mitra et al. [18] reported a rapid and high-yielding methodology for O-methylation of a library of phenols under microwave irradiation. Dimethyl sulfate was used as methylating reagent. The reactions were carried out in the presence of potassium carbonate in acetone as solvent (Scheme 3). The products were achieved in good to excellent yields.
Scheme 3: The reactions were carried out in the presence of potassium carbonate in acetone as solvent.
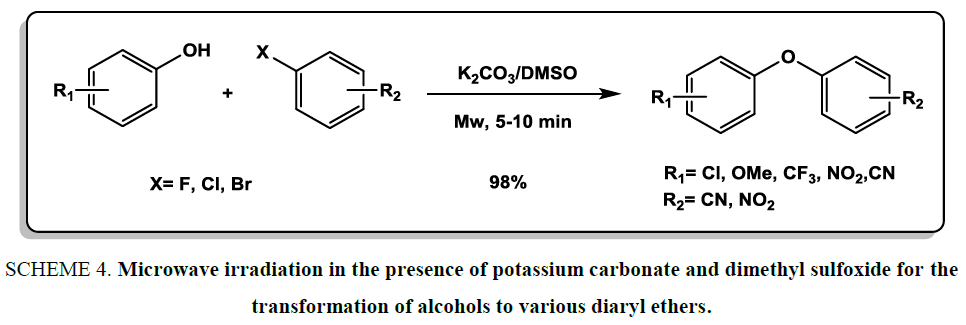
The coupling of alcohols with aryl halides is a general and useful route for the synthesis of diaryl ethers. In this regard, Li et al. [19] exploited microwave irradiation in the presence of potassium carbonate and dimethyl sulfoxide for the transformation of alcohols to various diaryl ethers Scheme 4. The SnAr reactions were performed in less than 10 min at room temperature.
Scheme 4: Microwave irradiation in the presence of potassium carbonate and dimethyl sulfoxide for the transformation of alcohols to various diaryl ethers.
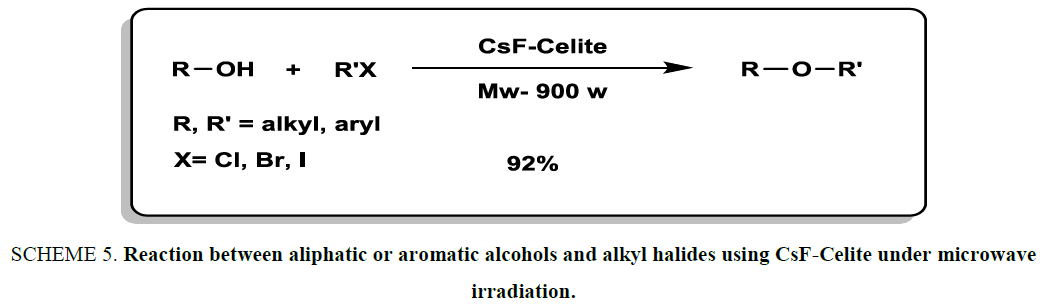
O-Alkylation was explored and accomplished by carrying out the reaction between aliphatic or aromatic alcohols and alkyl halides using CsF-Celite under microwave irradiation Scheme 5. [20]. CsF-Celite was acted both efficient catalyst and reaction medium. It is noteworthy that alkyl aryl sulfides were obtained in very excellent yields and appropriate times (2 min to 7 min).
Scheme 5: Reaction between aliphatic or aromatic alcohols and alkyl halides using CsF-Celite under microwave irradiation.
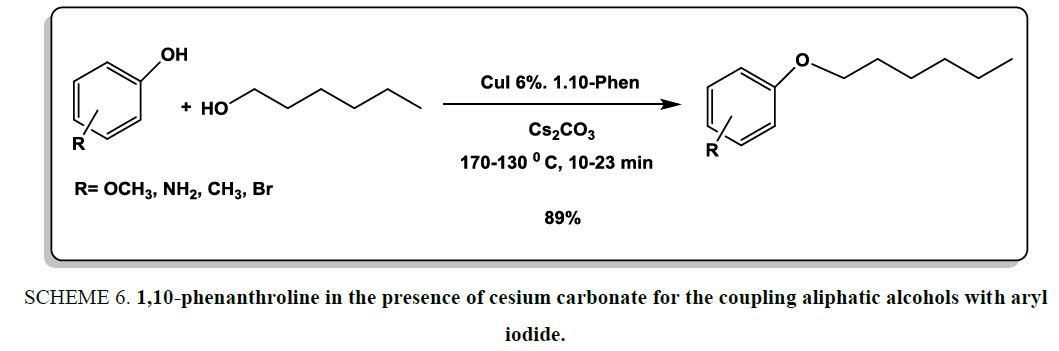
1,10-phenanthroline in the presence of cesium carbonate was designed as good and convenient system for the coupling aliphatic alcohols with aryl iodide [21]. Alkyl aryl ether derivatives were prepared using in high yields under microwave reaction conditions. To increase the efficiency of system, copper (I) iodide was added as catalyst into the reaction medium Scheme 6.
Scheme 6: 1,10-phenanthroline in the presence of cesium carbonate for the coupling aliphatic alcohols with aryl iodide.
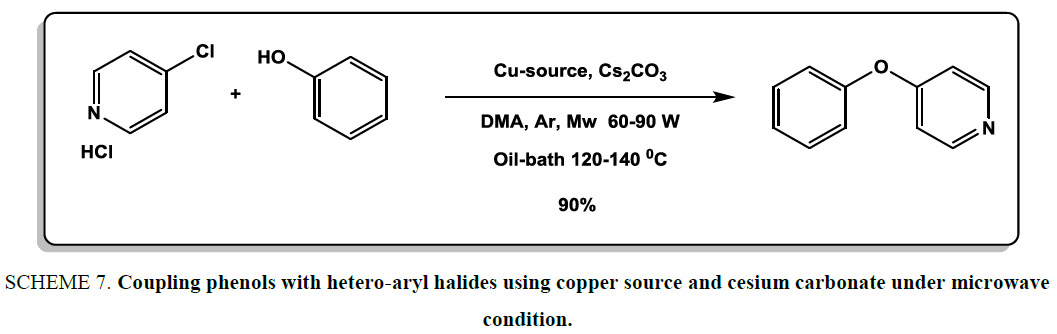
To synthesis of diaryl ethers, in the year of 2010, Benaskar et al. [22] surprisingly discovered that the coupling phenols with hetero-aryl halides could also be accomplished using copper source and cesium carbonate under microwave condition. Dimethylacetamide was used as solvent to carry out reactions Scheme 7. The high yield of products, simple isolation and mild reaction conditions demonstrated high efficiency of this methodology for the synthesis of diaryl ethers.
Scheme 7: Coupling phenols with hetero-aryl halides using copper source and cesium carbonate under microwave condition.
Conclusion
This short review focuses on the application of microwave technology in synthesis of ethers. Microwave is an efficient strategy toward the aim of green chemistry, and is recommended to use in organic transformations. Rapid reactions, high purity of products, less side-products, excellent yields, high reactivity, wider usable range of temperature, higher energy efficiency, sophisticated measurement, safety technology and modular systems enable changing from mg to kg scale are the best important advantages of this technology (use of microwave techniques in organic synthesis). In result, we foresee the development of major applications of microwave techniques for synthesis of organic compounds.
References
- Harkal S, Kumar K, Michalik D, et al. An efficient catalyst system for diaryl ether synthesis from aryl chlorides. Tetrahedron Letters. 2005;46:3237-40.
- Yu JL, Wang H, Zou KF, et al. Selective synthesis of unsymmetrical ethers from different alcohols catalyzed by sodium bisulfate. Tetrahedron. 2013;69:310-15.
- Paul S, Gupta M. Zinc-catalyzed Williamson ether synthesis in the absence of base. Tetrahedron Letters. 2004;45: 8825-29.
- Freedman HH, Bubois RA. An improved Williamson ether synthesis using phase transfer catalysis.Tetrahedron Letters. 1975;38:5251-3254.
- Branco J. Synthetic application of micellar catalysis. Williamson's synthesis of ethers. Tetrahedron Letters. 1988;44: 6677-80.
- Fuhrmann E, Talbiersky J.Synthesis of Alkyl Aryl Ethers by Catalytic Williamson Ether Synthesis with Weak Alkylation Agents. Org Process Res Dev. 2005;9:206-11.
- Verma S, Kumar N, Jain SL. Copper (II) Trans-bis-(glycinato): an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for cross coupling of phenols with aryl halides.Tetrahedron Letters. 2012;53(35):4665-68.
- Lin JM, Li HH, Zhou AM. Synthesis of Benzyl/Allyl Alkyl Ethers from Corresponding Magnesium Alkoxides. Tetrahedron Letters. 1996;37:5159-60.
- Sampath Kumar HM. Subba Reddy BV, Mohanty PK, et al. Clay catalyzed highly selective O-alkylation of primary alcohols with orthoesters. Tetrahedron Letters, 1997:38:3619-22.
- Salvatore RN, Smith RA, Nischwitz AK, et al. A mild and highly convenient chemo selective alkylation of thiols using Cs2CO3-TBAI. Tetrahedron Letters. 2005;46:8931-5.
- Ali Shah ST, Khan KM, Heinrich AM, et al. Cesium fluoride-Celite: A solid base for efficient syntheses of aromatic esters and ethers.Tetrahedron. 2005;61:6652-6.
- Gedye R, Smith F, Westaway K, et al. The use of microwave ovens for rapid organic synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986;27:279-82.
- Giguere RJ, Bray TL, Duncan SM, et al. Application of commercial microwave ovens to organic synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986;27:4945-8.
- Kappe CO, Dallinger D, Murphree SS. Practical microwave synthesis for organic chemists: Strategies, Instruments, and Protocols. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH; 2009.
- Gabriel C, Gabriel S, Grant EH, et al. Dielectric parameters relevant to microwave dielectric heating. Chem Soc Rev. 1998;27:213-24.
- Wang JX, Zhang M, Xing Z, et al. Synthesis of Aromatic Ethers without Organic Solvent and Inorganic Carrier under Microwave Irradiation. Syn Commun. 1996;26:301-5.
- Bogda? D, Pielichowski J, Jaskot K. A rapid williamson synthesis under microwave irradiation in dry medium. Org Prep ProcInt.1998;30: 427-32.
- Mitra KA, De A, Karchaudhuri N. Microwave enhanced synthesis of aromatic methyl ether. Indian J Chem. 2000;39B:387-9.
- Li F, Wang Q, Ding Z, et al. Microwave-Assisted synthesis of diaryl ethers without catalyst. Org let. 2003;5:2169-71.
- Polshettiwar V, Kaushik MP. Microwave enhanced chemistry of CsF-Celite: an efficient catalyst for the synthesis of esters, Ethers, and their thio-analogues. Cat Commun. 2005;6(3):191-4.
- Rukmini E, Taylor RT. Microwave assistance in the copper-catalyzed reactions of aliphatic alcohols with aryl iodides.Int Electron Conf SynthOrg Chem. 2009;13:1-5.
- Benaskar F, Patil NG, Meuldijk J, et al. Copper (0) in the Ullmann heterocycle-aryl ether synthesis of 4-phenoxypyridine using multimode microwave heating. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010;51:248-51.