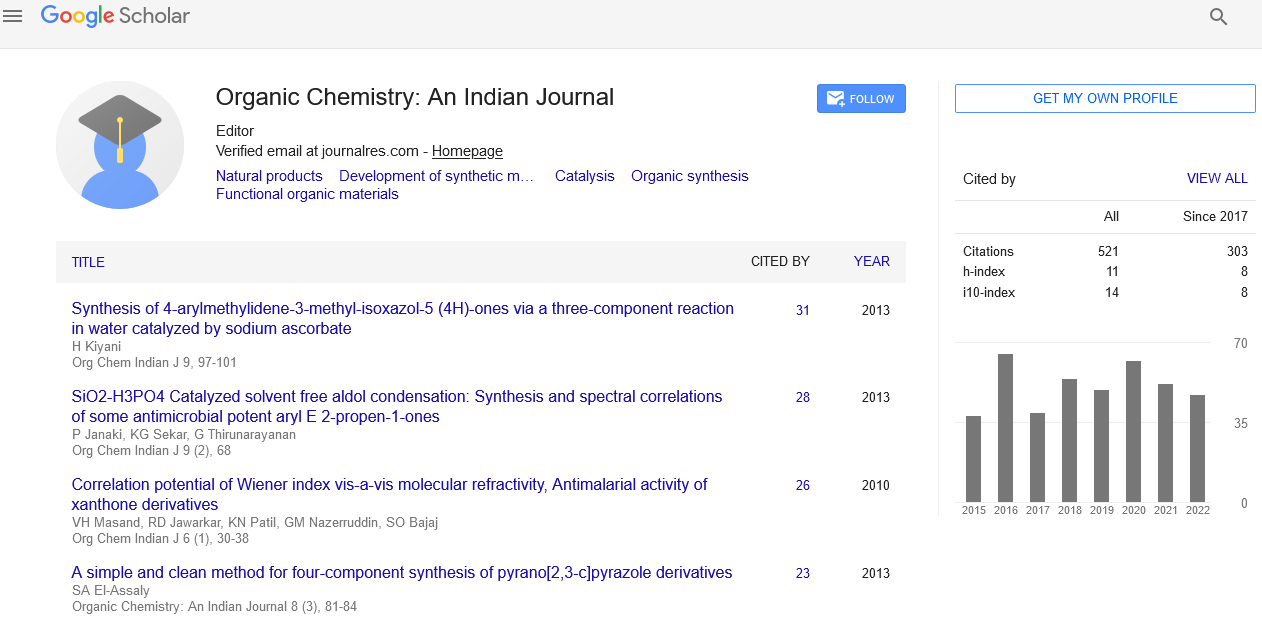
Abstract
Studies of CO2 corrosion inhibition properties of alkanolamine molecules by electrochemical and molecular modelling for the preservation of 1Cr steel
Author(s): Belle TaylorCarbon and low alloy steels are the most widely used materials in oil and gas production/transmission infrastructure despite their susceptibility to CO2 corrosion. This is because of their relatively low cost, availability, mechanical properties, simplicity of construction, and cost-effectiveness through corrosion inhibition. Iron dissolving is caused by electrochemical reactions that take place between the steel surface and the aqueous phase when CO2 dissolves in water and hydrates carbonic acid (H2CO3). Corrosion by-products or mineral scales can form on the surface under certain conditions, which is likely to have a substantial impact on the corrosion mechanism (s). Although this electrochemical process has been studied for more than 40 years, the main focus of research continues to be the corrosion mechanisms at the metal-electrolyte interface.