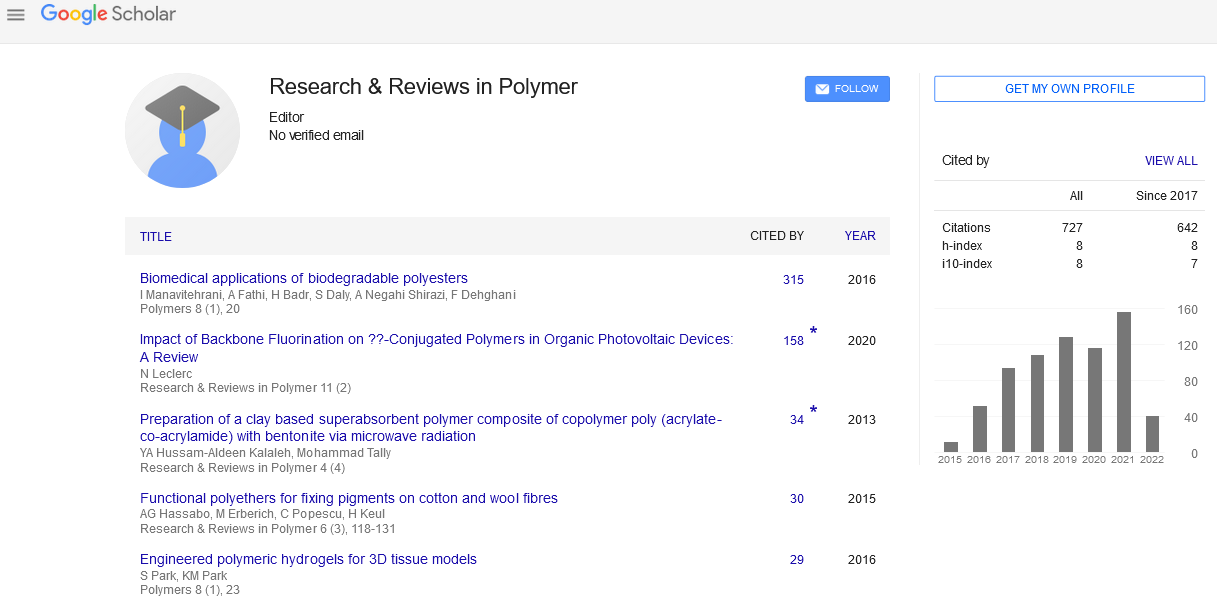
Abstract
Polycationic polymers and drugs: Investigations into interactions between acyclovir and polymers
Author(s): Rotraut Stephanie Muller, Anke OstmannIn the development of drug formulations interactions between contents may play an important role. It was the aim of our present studies to investigate into drug-polymer interactions. Interaction of the antiviral drug acyclovir with polyethylenimines, polyvinylamines and the non-ionic PVP was investigated using amodified equilibriumdialysis. Themembrane was permeable only to free acyclovir, while polymers and acyclovir-polymer-associates did not pass through. Significant amounts of acyclovir were bound with the polyethylenimines. The formation of associates consisting of acyclovir and PVP or polyvinylamine could not be demonstrated. In solutions of acyclovir and polyethylenimine (Mr=25000) the amount of bound drug is increased with increasing concentration of acyclovir. Between 7.9 µg and 31.7 µg take part in the formation of associates. Differences in the osmotic pressure of the solutions do not play an important role in the permeation of acyclovir. In solutions containing acyclovir and highmolecular weight polyethylenimine (Mr=750000) the bound amount of drug increaseswith increasing acyclovir concentration up to c0=400µg/100 ml. A further increase does not change the amount of bound drug significantly. Possibly, the binding capacity is reached. Molecular modeling investigations were performed.According to the calculations, about 85% of the interactions can be attributed to electrostatic interactions.